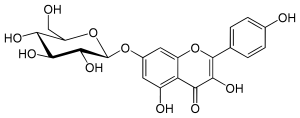
Kaempferol 7-O-glucoside
Appearance
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
7-(β-D-Glucopyranosyloxy)-3,4′,5-trihydroxyflavone
| |
| Systematic IUPAC name
3,5-Dihydroxy-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-7-{[(2S,3R,4S,5S,6R)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxan-2-yl]oxy}-4H-1-benzopyran-4-one | |
| Other names
Kaempferol-7-O-beta-D-glucoside
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C21H20O11 | |
| Molar mass | 448.380 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Kaempferol 7-O-glucoside is a flavonol glucoside. It can be found in Smilax china,[1] and in the fern Asplenium rhizophyllum, and its hybrid descendants, as part of a complex with caffeic acid.[2]
Derivatives
[edit]Amurensin is the tert-amyl alcohol derivative of kaempferol 7-O-glucoside. 6'''-O-acetyl amurensin is found in the leaves of Phellodendron japonicum.[3]
References
[edit]- ^ Xu, W.; Liu, J.; Li, C.; Wu, H. Z.; Liu, Y. W. (2008). "Kaempferol-7-O-β-d-glucoside (KG) isolated from Smilax china L. rhizome induces G2/M phase arrest and apoptosis on HeLa cells in a p53-independent manner". Cancer Letters. 264 (2): 229–240. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2008.01.044. PMID 18343026.
- ^ Harborne, Jeffrey B.; Williams, Christine A.; Smith, Dale M. (1973). "Species-specific kaempferol derivatives in ferns of the Appalachian Asplenium complex". Biochemical Systematics and Ecology. 1 (1): 51–54. doi:10.1016/0305-1978(73)90035-5.
- ^ Chiu, C. Y.; Li, C. Y.; Chiu, C. C.; Niwa, M.; Kitanaka, S.; Damu, A. G.; Lee, E. J.; Wu, T. S. (2005). "Constituents of Leaves of Phellodendron japonicum MAXIM. And Their Antioxidant Activity". Chemical & Pharmaceutical Bulletin. 53 (9): 1118. doi:10.1248/cpb.53.1118.
